In an era where power outages seem to be increasingly common, finding a reliable and sustainable backup energy solution is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Traditional gas generators have long been the go-to, but a cleaner, quieter, and more versatile option has emerged: the solar generator. These portable power stations, combined with solar panels, offer a fantastic way to keep essential appliances running. However, the real power and convenience come when you learn the proper steps for Integrating Solar Generators with Home Electrical Systems. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from the basic components to advanced installation and critical safety precautions.
Understanding the Components of a Solar Generator System
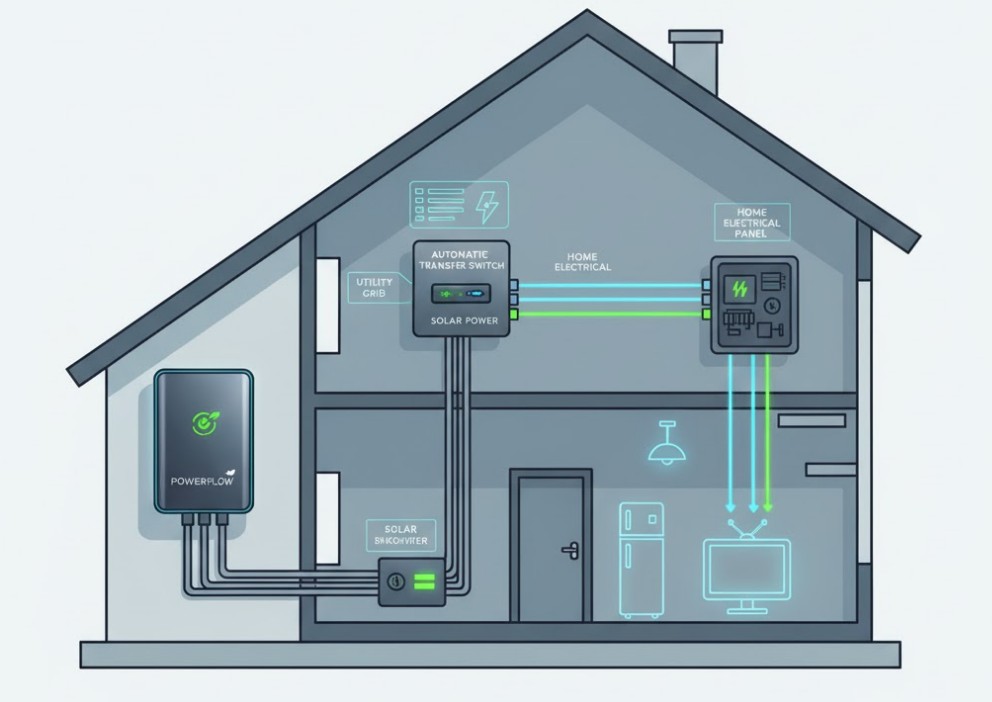
Before diving into the integration process, it is essential to understand what a solar generator truly is and the key components that make it work. A common misconception is that it “generates” power like a gas engine; instead, it stores energy. In simple terms, a solar generator is a battery-based system that captures, converts, and stores solar energy.
The Four Pillars of the Solar Generator
- Solar Panels: These collect sunlight (photons) and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. They are the input source for your clean energy. Interestingly, kids can learn more about how solar technology is a key solution to climate change.
- Charge Controller: This component regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the battery, preventing overcharging and maximizing battery life.
- Battery (Energy Storage): This is the heart of the system, storing the DC power collected from the panels. Most modern units use advanced, lightweight lithium-ion batteries.
- Inverter: Because most household appliances run on alternating current (AC), the inverter converts the DC power stored in the battery into usable AC power. Understanding what a solar inverter is is crucial for efficient system integration.
These four elements work in concert to provide portable, on-demand power. Furthermore, their modular nature makes them an excellent candidate for semi-permanent integration with your existing home wiring.
Why Integrate Your Solar Generator? Convenience vs. Safety
Using a solar generator purely as a portable power station—running extension cords to individual appliances—is functional but inefficient. True peace of mind comes from connecting it directly to your home’s electrical system. This allows you to power dedicated circuits, like your kitchen, well pump, or specific lighting circuits, without a web of cords.
The Critical Role of the Transfer Switch
Connecting any generator—gas or solar—to your home’s wiring requires a device called a transfer switch. This is not optional; it is a critical safety and legal requirement. The transfer switch serves one indispensable purpose: to prevent backfeeding. Backfeeding occurs when power flows from your generator back out to the main utility grid. This is immensely dangerous, as it can electrocute utility workers attempting to repair lines. Therefore, the transfer switch physically isolates your home from the main utility grid before the generator power is introduced.
There are two primary types of transfer switches suitable for this application:
- Manual Transfer Switch (MTS): Requires you to physically flip a switch to disconnect from utility power and connect to generator power. This is the most common and cost-effective method for solar generator integration.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): Detects a power outage and automatically switches the home from utility power to generator power. While convenient, an ATS is typically more complex and costly, usually reserved for whole-house standby generators.
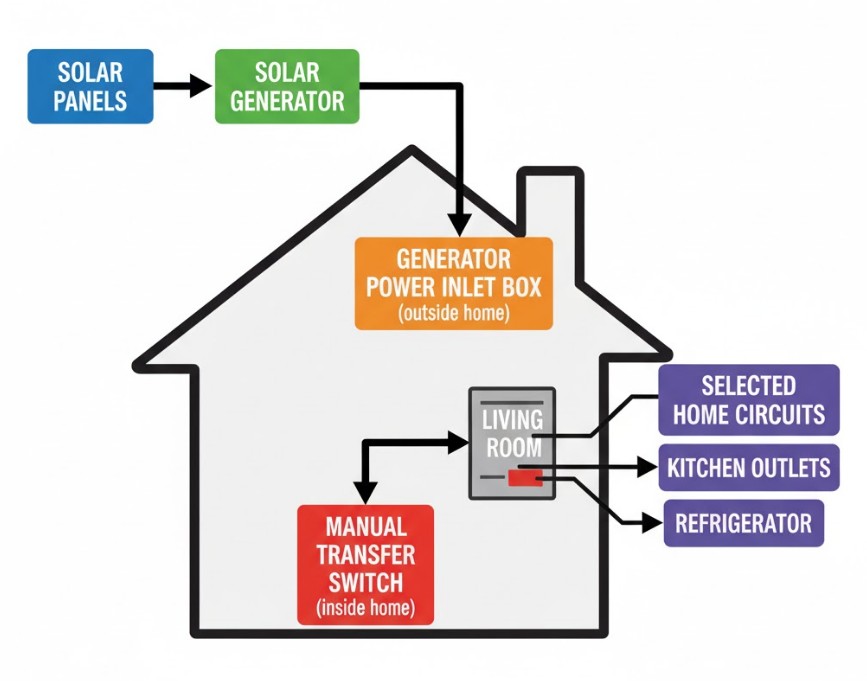
Step-by-Step Guide to Integration with an MTS (Recommended Method)
The manual transfer switch (MTS) is the safest and most practical way for a homeowner to integrate a portable solar generator. Because solar generators are generally not designed for “whole-house” power (though large models are emerging), an MTS panel focuses power on a few selected, critical circuits.
Step 1: System Sizing and Circuit Selection
Before purchasing or installing anything, you must determine what you need to power. Create a list of essential items (e.g., refrigerator, specific lights, a solar generator for a refrigerator, internet router, furnace fan). Calculate the total running watts and the surge (starting) watts for all these items. This will tell you the minimum capacity your solar generator and MTS panel must handle. For example, if your total need is around 2500W, you might look into the best 3000-watt solar generators.
Step 2: Installation of the Manual Transfer Switch (MTS)
Note: This work should always be performed by a licensed electrician to ensure safety and compliance with local electrical codes.
The electrician will install the MTS panel near your existing main electrical panel. Wires from your selected critical circuits are rerouted from the main panel through the MTS. The MTS is connected to a special outdoor Generator Power Inlet Box. This box is where you plug in your solar generator.
Step 3: The Generator Power Inlet Box
This outdoor, weatherproof box houses a specialized inlet receptacle. The size and shape of this receptacle are dictated by the maximum power output of your solar generator (e.g., a 30A or 50A twist-lock connection). The key function is to provide a safe, secure, and permanent connection point for your generator cable, ensuring it is isolated from weather and accidental contact.
Step 4: Making the Connection and Powering Up
During an outage, the process is straightforward:
- Wheel your solar generator into a secure, dry, and well-ventilated area (even though they don’t produce carbon monoxide, they should be accessible). Remember to review how to secure a generator, as theft can be a concern.
- Connect the appropriate heavy-duty power cord from the solar generator’s AC output port to the outdoor Generator Power Inlet Box.
- Inside, at the MTS panel, the electrician will have set up the procedure. Typically, you must turn off the main utility breaker, then flip the main switch on the MTS from “Line” (Utility) to “Gen” (Generator).
- Finally, turn on the individual circuit breakers on the MTS panel for the essential circuits you need to power.
Critical Safety and Technical Considerations
When dealing with home electricity, safety is paramount. Integrating Solar Generators with Home Electrical Systems involves more than just plugging things in; it requires adherence to strict guidelines.
Understanding Grounding and Bonding
Most portable solar generators are designed as “floating neutral” or “ungrounded” systems. When connecting to a home’s electrical system via a transfer switch, the generator must become a “separately derived system” for safety. The transfer switch handles this critical process, ensuring that the neutral and ground wires are handled correctly to prevent electrical shocks and appliance damage. Always confirm with your electrician that the MTS is properly installed and that the neutral and ground are correctly handled according to the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Pure Sine Wave Output is Essential
A high-quality solar generator will provide a pure sine wave AC output. This is vital for modern electronics, sensitive appliances, and anything with a motor (like your refrigerator or furnace fan). Cheaper generators might output a “modified sine wave” or “square wave,” which can damage sensitive electronics and cause motors to run hot, eventually leading to failure. When selecting a unit for home integration, ensure it specifies pure sine wave inverter technology.
Managing Total Load and Generator Overload
Just because your generator has a maximum wattage doesn’t mean you should run it at that level constantly. Always manage your load. For example, avoid simultaneously starting a refrigerator, a well pump, and a microwave. Staggering the start-up of high-draw appliances protects the solar generator’s inverter from being overloaded by the cumulative surge wattage. Remember the system sizing exercise in Step 1—adherence to those calculations is key to longevity and reliable operation.
Optimizing Your Solar Generator Setup for Maximum Runtime
The beauty of a solar generator system is its ability to be recharged during an extended outage, provided there is sunlight. Optimization is about maximizing that recharging and minimizing energy waste.
Panel Placement and Angle
For the longest runtimes, your solar panels must be positioned for maximum sun exposure. This usually means a south-facing (in the Northern Hemisphere) location that is free of shade from trees or buildings. Adjusting the tilt angle to match the season’s sun path can dramatically increase the energy harvest. Investing in longer extension cables for the solar panels allows you to place the generator itself in a more secure or convenient location while keeping the panels in the sun.
Efficiency and Standby Power
When operating on generator power, every watt counts. Unplug devices that draw phantom power or standby power, such as phone chargers, televisions, and desktop monitors that are turned off but still plugged in. Using LED lighting instead of incandescent bulbs is also a small change that yields significant energy savings, extending the battery life of your system by hours.
Beyond Basic Backup: Advanced Applications
The flexibility of a modern solar generator allows for applications beyond just emergency backup. Their silent operation and clean power make them suitable for sophisticated uses.
Off-Grid Redundancy and Hybrid Systems
For homes with existing rooftop solar (grid-tied without battery backup), a solar generator provides essential redundancy. When the grid goes down, grid-tied systems shut off for safety. The portable solar generator acts as a separate, self-contained energy island. Some advanced models can even accept input from the main solar array (with the correct accessories and professional installation), turning a portable unit into a crucial part of a larger hybrid energy strategy.
Powering Remote Structures and Workshops
While this article focuses on the main house, the silent, zero-emission nature of these units makes them ideal for powering remote sheds, workshops, or detached offices without the need to run expensive, permanent wiring from the main house. The principles of safe connection (using appropriate outlets and grounding) remain the same, even in a standalone structure.
The technology for solar generators is advancing rapidly, particularly in battery chemistry and inverter efficiency. Today’s systems offer lighter weights, faster charging times, and greater depth of discharge (DoD) for longer battery life compared to models from just a few years ago. As you plan your integration, consider a slightly larger unit than your current needs to accommodate future expansion or the addition of a new critical appliance. Future-proofing your system is a wise investment.
A final note on the practical steps of integrating solar generators with home electrical systems revolves around legality and liability. In many jurisdictions, any work involving the main electrical panel and a permanently mounted transfer switch requires a permit and inspection. Ignoring these rules can lead to serious safety hazards, void your homeowner’s insurance, and result in fines. A licensed electrician will ensure the installation adheres to all local codes, including the critical National Electrical Code (NEC) standards for grounding, wire gauge, and the physical mounting of the components. Their expertise is invaluable in correctly sizing the MTS and the feeder cable to match the continuous output of the solar generator, preventing thermal overload and fire risk. The upfront cost of professional installation is minimal compared to the peace of mind and safety it provides. Furthermore, having a professional stamp of approval on the system confirms that the required electrical isolation is correctly achieved, protecting utility workers from the dangers of backfeeding.
The battery is the most expensive and arguably most critical component of a solar generator. Proper care is essential to maximize its lifespan and maintain its readiness for an outage. Modern lithium-ion batteries are robust, but they do require thoughtful maintenance.
For long-term storage, experts recommend keeping the solar generator’s battery at a State of Charge (SoC) between 50% and 80%. Storing a lithium battery at a full 100% for extended periods can accelerate degradation, reducing its total available capacity over time. Similarly, allowing the battery to completely discharge (0% SoC) frequently is detrimental. For a unit dedicated to home backup, consider connecting a small maintenance solar panel or occasionally plugging the unit into a wall outlet to “top off” the charge and keep it within the optimal range. This proactive approach ensures the generator is ready to deliver maximum power when a sudden outage occurs.
The operating temperature of the solar generator significantly affects its performance and lifespan. Avoid storing or operating the unit in extreme heat or cold. While the unit itself might be plugged in outdoors to the inlet box during an outage, the battery unit should ideally be kept in a temperature-controlled environment, such as a garage or utility room, especially during extended use or charging. High temperatures, in particular, are the enemy of lithium-ion batteries, accelerating the internal chemical breakdown. Moreover, ensure that the unit’s cooling vents are never blocked. This is particularly important when operating the solar generator at or near its maximum output, as the inverter and battery management system generate significant heat that must be dissipated to maintain efficiency and safety.
The meticulous planning, professional installation, and disciplined maintenance required for Integrating Solar Generators with Home Electrical Systems transform a portable device into a robust, essential component of your home’s infrastructure. By embracing this clean, quiet technology and following the necessary safety steps, you are not just preparing for the next power outage—you are taking a significant step towards energy independence and a more sustainable future.
Final Thoughts
The transition from relying solely on the utility grid to having a powerful, clean, and seamlessly integrated backup system is one of the smartest investments a homeowner can make today. Solar generators offer a pathway to silent operation, zero emissions, and the freedom to recharge indefinitely using the sun. By taking the time to correctly size your system, utilizing a professional to install the mandatory manual transfer switch and inlet box, and committing to proper maintenance, you ensure that your home remains operational, safe, and comfortable when the lights go out. The future of reliable home power is here, and it is powered by the sun.
Amranul is a highly experienced product review writer with a passion for helping readers make smart, informed purchasing decisions. Since 2018, he has specialized in thoroughly researching and analyzing a wide range of products to deliver honest, in-depth reviews. Amranul combines technical accuracy with clear, engaging writing to break down complex product features and highlight true user value. Look for his reviews to find reliable information and expert insights you can trust before you buy!





