Modern portable and standby generators often include a CO (Carbon Monoxide) sensor that automatically shuts down the engine when carbon monoxide levels become dangerously high. This feature is designed to prevent poisoning, but occasionally, users encounter sensor malfunctions that cause their generator to stop even when the air is safe. Because of this, some people search for ways to bypass the CO sensor on a generator.
However, before considering such an action, it’s essential to understand what the CO sensor does, the potential risks of tampering with it, and the legal and safety implications. This article will cover every detail you need to know — from understanding CO sensors and troubleshooting false alarms to safer alternatives instead of bypassing the sensor entirely.

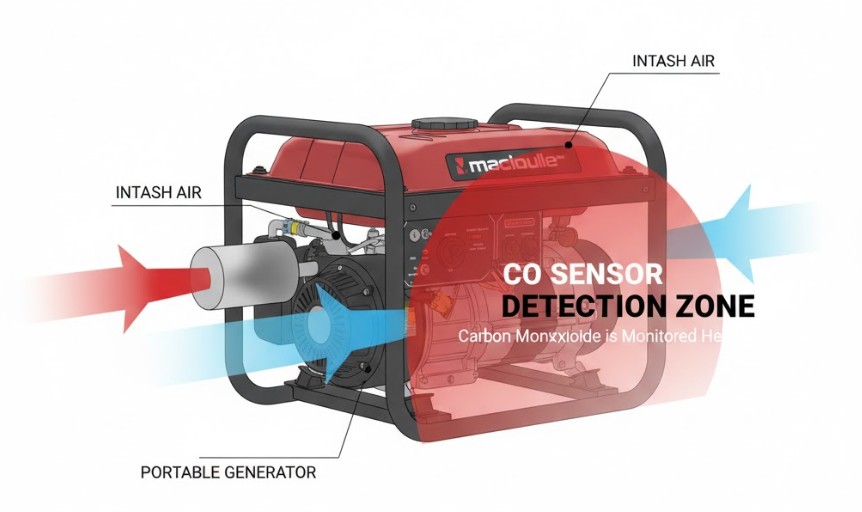
What Is a CO Sensor on a Generator?
The CO sensor (Carbon Monoxide sensor) is a built-in safety device designed to detect the presence of carbon monoxide gas in the surrounding area. When this invisible and odorless gas reaches a critical level, the sensor automatically shuts off the generator to protect users from poisoning.
Carbon monoxide is a silent killer — inhaling it for just a few minutes in a confined area can lead to serious health effects, unconsciousness, or even death. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), hundreds of people die each year from accidental CO poisoning, and many more are hospitalized.
How It Works
- The sensor continuously monitors air quality near the generator’s exhaust system.
- If CO levels exceed the safety threshold (typically 70 ppm or higher), it triggers an automatic shutdown.
- Some models also flash a warning light or emit a beeping alarm before shutting off.
This feature, though sometimes inconvenient, is crucial for preventing fatal accidents.
Why Do People Want to Bypass the CO Sensor?
Many generator owners report issues such as the unit shutting down too soon or refusing to start, especially in humid or dusty environments. These problems are often blamed on a faulty CO sensor.
Common Reasons Include:
- Sensor Malfunction: Dust, debris, or moisture can cause false alarms or sensor failure.
- Frequent False Shutdowns: The generator may shut off even when operating outdoors with sufficient ventilation.
- Lack of Replacement Parts: Some older generator models may not have easily available replacement sensors.
- Emergency Situations: Users in remote areas without power might consider bypassing the sensor temporarily to restore functionality.
While these reasons may sound understandable, bypassing the CO sensor is never a recommended long-term solution.
The Dangers of Bypassing a CO Sensor
Bypassing the CO sensor removes an essential layer of protection. Carbon monoxide can accumulate quickly, especially when a generator is used near enclosed spaces, garages, or tents.
Major Risks Include:
- CO Poisoning: Exposure can cause dizziness, nausea, confusion, and death in severe cases.
- Legal Liability: Tampering with safety equipment may void your warranty and violate safety regulations.
- Fire and Explosion Hazards: Improper wiring or modifications could lead to electrical short circuits.
- Reduced Resale Value: A modified generator may lose its compliance certification, making resale difficult.
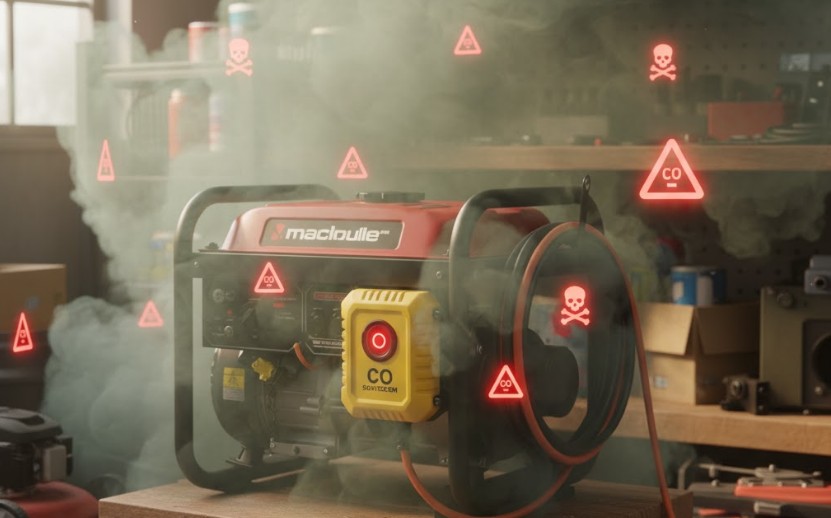

How the CO Sensor Affects Generator Operation
Understanding how the CO sensor interacts with the generator’s electronics helps identify why false shutdowns occur. Most modern generators have the CO sensor integrated into the control circuit. When high CO is detected, it sends a signal that cuts power to the ignition coil or fuel system, forcing an immediate stop.
Typical Symptoms of a Faulty CO Sensor
- Generator starts and stops after a few seconds.
- Warning light stays on even after resetting.
- No-start condition with spark but no fuel delivery.
- CO alarm activates in open-air operation.
If you experience any of these, it might indicate a defective CO sensor rather than actual CO presence.
Before You Consider Bypassing: Safe Troubleshooting Steps
Instead of jumping directly into bypassing, try these safer diagnostic methods first:
1. Inspect and Clean the Sensor Area
Dirt, insects, or oil residue may obstruct the sensor. Use a soft brush or compressed air to gently clean around the sensor housing.
2. Test in Different Locations
Move the generator to an open outdoor space to ensure proper airflow. Avoid using it under awnings or close to walls.
3. Check the Exhaust Direction
Ensure the exhaust pipe is facing away from windows or structures where CO might accumulate and trigger false detection.
4. Replace the CO Sensor (If Possible)
Some generator brands sell replacement CO sensors as standalone components. This is a much safer fix than bypassing.
5. Reset the Generator’s Control Module
Disconnect the spark plug and battery, then wait a few minutes before reconnecting to reset the control system.
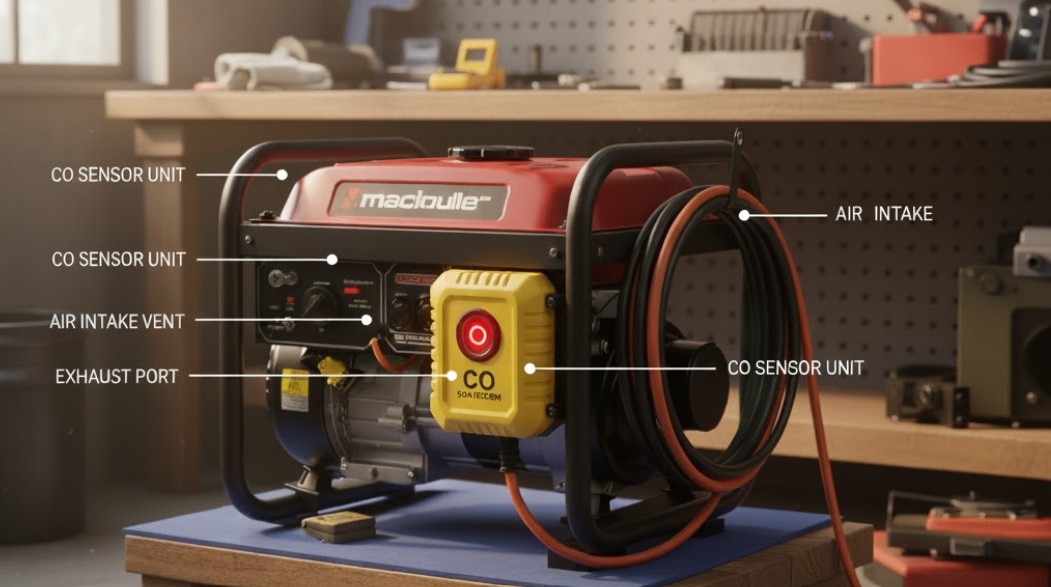

Understanding the CO Sensor Wiring
In most generators, the CO sensor has two or three wires connected to the control board. Typically, these include:
- Power (often 5V or 12V)
- Ground
- Signal wire (to shutoff circuit)
When CO is detected, the signal wire changes voltage or resistance, triggering the shutdown relay. Disabling or cutting these wires might prevent the signal from reaching the control board — effectively bypassing the sensor. However, doing this permanently can create severe safety and warranty issues.
Legal and Safety Concerns
Bypassing or tampering with emission or safety systems may violate federal or state regulations in many regions. Manufacturers like Honda, Generac, and Champion explicitly warn users not to modify their equipment.
Instead, if your generator is shutting down unexpectedly, contact customer service or an authorized repair technician for inspection.
Alternative Solutions Instead of Bypassing
Rather than disabling your CO sensor, here are safer alternatives to ensure uninterrupted operation:
1. Install an External CO Detector
Place a carbon monoxide detector near your generator’s operation zone. This gives additional monitoring without disabling the built-in safety feature.
2. Create a Ventilated Shelter
If weather is causing sensor problems, construct a small roofed shelter with open sides. This protects the generator while maintaining airflow.
3. Regular Maintenance
Keep the generator clean, check spark plugs, air filters, and ensure there’s no exhaust blockage. Clean engines emit fewer gases, reducing CO build-up.
4. Use Natural Gas Generators
Natural gas generators emit significantly lower levels of carbon monoxide compared to gasoline ones. If you often face CO issues, consider switching. Learn more about this in this detailed guide on natural gas generator compatibility.
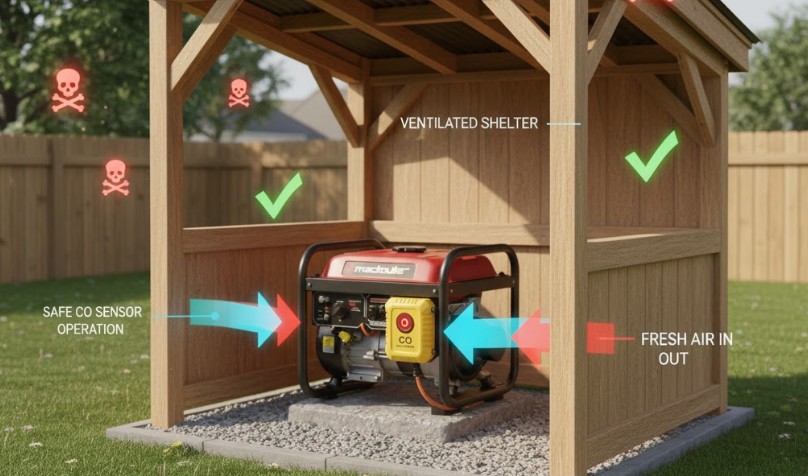

Can You Temporarily Bypass the CO Sensor for Testing?
In some rare cases, technicians temporarily bypass the CO sensor only for controlled testing or troubleshooting. This should only be done:
- In open-air conditions, away from living areas.
- By experienced professionals who understand electrical schematics.
- With CO detectors actively monitoring nearby air.
Once diagnostics are complete, the sensor should always be reconnected to restore safety functionality. Never operate a generator long-term without it.
Upgrading or Replacing Your Generator
If your CO sensor fails repeatedly or your generator is outdated, replacing the entire unit might be a safer and more cost-effective decision. Newer models feature advanced CO shutdown technology, improved insulation, and better air intake systems.
Additionally, consider if upgrading to a standby or whole-house generator suits your needs. It could even improve your home’s resale value. For more insights, check out this guide on how a whole-house generator adds value to your home.
Key Safety Reminders
- Never run a generator indoors, in garages, or near windows.
- Keep at least 20 feet of distance between the generator and your home.
- Install CO alarms inside your living spaces for added protection.
- Do not modify, cut, or disable any safety feature without understanding the full risk.
- Follow the manufacturer’s user manual and warranty conditions.
Environmental Considerations
Beyond human safety, generators contribute to environmental emissions. A malfunctioning or modified generator can release excessive CO, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, harming local air quality. Maintaining the CO sensor ensures compliance with environmental standards and keeps emissions under control.
Proper Disposal and Recycling
If replacing a faulty sensor or generator, dispose of the old parts responsibly at a local recycling center or authorized waste collection site. Never throw electronics or sensors in regular trash bins.
Maintenance Tips for Longer CO Sensor Life
- Store your generator in a dry, clean place when not in use.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to rain or humidity.
- Start the generator periodically to prevent corrosion.
- Clean the air intake and exhaust vents regularly.
- Replace the CO sensor every 3–5 years or as recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is it legal to bypass the CO sensor on a generator?
No. It is considered tampering with a safety system and may void your warranty or violate federal emission laws.
2. What should I do if my generator keeps shutting down because of the CO sensor?
Try cleaning or replacing the sensor, moving the generator outdoors, or consulting a technician before considering any modification.
3. Can weather conditions affect CO sensor readings?
Yes. Excess humidity, rain, or dust can trigger false alarms. Always operate in a dry, ventilated space.
4. Are there generators without CO sensors?
Older models may not have built-in CO protection, but most modern ones do. If using an older unit, install an external CO detector nearby.
5. How do I know if my CO sensor is faulty?
If your generator shuts off unexpectedly in open air, shows persistent warning lights, or fails to restart, it may indicate a defective sensor.
Final Thoughts
While it may be tempting to learn how to bypass the CO sensor on a generator, the truth is that doing so introduces far more danger than benefit. The sensor exists to protect you and your family from an invisible and lethal gas. Instead of disabling it, focus on maintaining your generator properly, keeping it in well-ventilated areas, and replacing faulty sensors when necessary.
If you rely heavily on backup power, consider upgrading to a safer, modern generator model that includes enhanced CO detection and shutdown systems. Remember: power convenience should never come at the cost of safety.
Stay safe, stay informed, and keep your generator running efficiently — the right way.
Amranul is a highly experienced product review writer with a passion for helping readers make smart, informed purchasing decisions. Since 2018, he has specialized in thoroughly researching and analyzing a wide range of products to deliver honest, in-depth reviews. Amranul combines technical accuracy with clear, engaging writing to break down complex product features and highlight true user value. Look for his reviews to find reliable information and expert insights you can trust before you buy!





