The simple and resounding answer is: Yes, a generator can absolutely run on natural gas. In fact, for many homeowners and businesses, a natural gas generator is often the most practical, convenient, and reliable source of backup power. Unlike gasoline or propane which require on-site storage tanks and frequent refueling, natural gas is delivered directly through an underground utility line. This crucial difference makes it an incredibly appealing fuel source, especially for long-duration power outages. But what makes these generators tick, and are they the right choice for you?
This comprehensive guide will explore how natural gas generators work, their unique advantages and disadvantages, and the different types available on the market. Furthermore, we will delve into the critical aspects of installation, efficiency, and safety, providing you with all the information you need to make an informed decision.
The Mechanics of a Natural Gas Generator
At its core, a generator is an engine that turns chemical energy into electrical energy. While the general principle is the same across all fuel types, there are specific differences when an engine is designed to run on natural gas.
How the Fuel System Differs
Unlike liquid fuels that require a carburetor or fuel injectors to atomize the fuel, natural gas is already in a gaseous state. This requires a slightly different delivery system. The gas flows from the utility line, passes through a regulator to control pressure, and then enters a specialized mixing chamber or carburetor designed for gas. The mixture of natural gas and air is then compressed and ignited in the engine’s cylinders, driving a piston and turning the alternator to produce electricity. Because the fuel delivery is constant and automatic, these generators are often designed for long-term continuous operation.
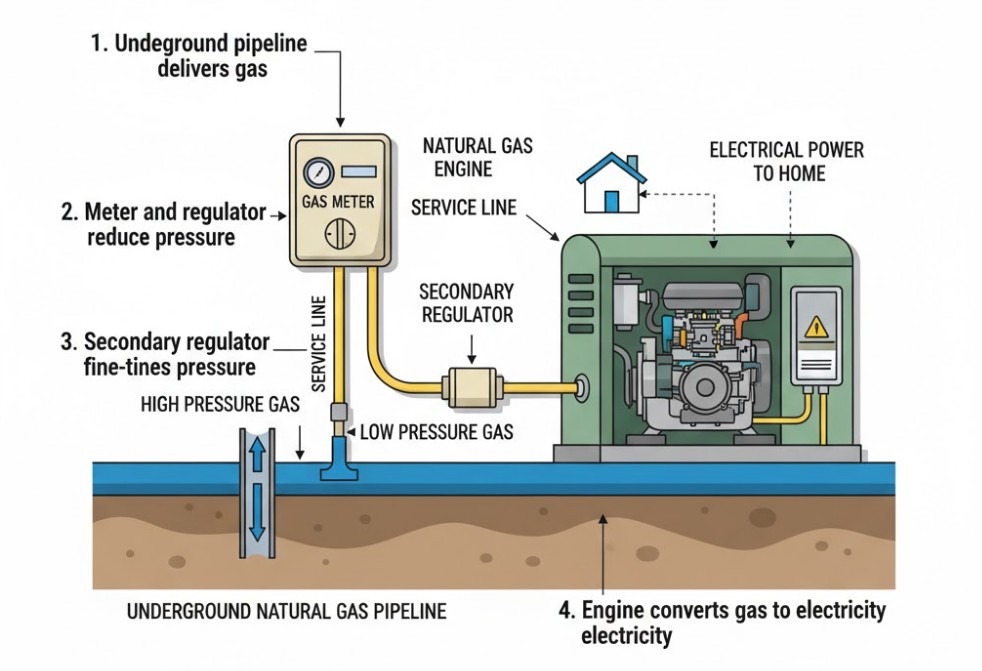
Why Natural Gas is a Preferred Generator Fuel
The popularity of natural gas as a fuel source for generators stems from several powerful advantages, especially when compared to its liquid counterparts like gasoline and diesel.
Uninterruptible Fuel Supply
The most significant benefit of a natural gas generator is its unlimited run time. When a power outage strikes, gasoline or propane generators are limited by the fuel you have stored. Once the tank is empty, the generator stops, and you must manually refuel it. Natural gas, however, is piped directly into your home or business. Since the pipes are often buried underground, they are less susceptible to disruption from severe weather like ice storms or hurricanes. This provides a truly continuous power solution during prolonged emergencies, giving you peace of mind.
Cleaner Emissions and Environmental Impact
Natural gas primarily consists of methane, a hydrocarbon that burns much cleaner than liquid fuels like diesel or gasoline. The combustion process results in lower emissions of carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This makes natural gas generators a more environmentally friendly choice and often means they comply more easily with strict air quality regulations. Furthermore, the clean-burning nature reduces soot buildup and wear and tear on the engine, potentially extending the generator’s lifespan.
If you’re exploring different types of backup power, you might be interested in the versatility of generators that can use more than one fuel. Explore the options for liquid and gaseous fuel generators here: Best Dual Fuel Generators.
Cost and Convenience
Over the long term, natural gas can be a more cost-effective fuel source than gasoline or propane, depending on local utility prices. More importantly, the sheer convenience of never having to haul heavy fuel canisters or monitor tank levels cannot be overstated. When the power goes out, the generator simply turns on, and when the power returns, it shuts off—all automatically. This hands-off operation is a major benefit for both residential and commercial users.
Types of Natural Gas Generators
When shopping for a generator that runs on natural gas, you will typically encounter three main categories, each serving a different need.
1. Standby Generators (Primary Use)
These are the most common type of natural gas generator. Standby generators are permanently installed outside the home or business, much like an air conditioning unit. They are connected directly to the home’s electrical system and the natural gas line. They are equipped with an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) which constantly monitors utility power. When the main power fails, the ATS signals the generator to start up and transfers the electrical load within seconds. Once utility power is restored, the ATS switches the load back and turns the generator off. They are the definition of “set it and forget it” backup power.
Looking for a permanent, reliable backup solution? See our top picks for residential units: Best Natural Gas Portable Generators
2. Portable Generators (Limited Use)
While most portable generators run on gasoline, there are models designed specifically to run on or be converted to run on natural gas. These models, however, are not self-starting and must be manually connected to a natural gas source, usually an outdoor low-pressure utility connection or a conversion kit. While they offer the advantage of mobility and can be cheaper upfront, they require manual operation and typically have smaller power outputs than standby units. They are often best suited for smaller, short-term needs or as job-site power.
3. Multi-Fuel Generators (Dual and Tri-Fuel)
For maximum flexibility, many generators are designed as multi-fuel models. These can switch between two or even three fuel sources—typically gasoline, propane, and natural gas. This offers an excellent compromise: you can use the convenience of the natural gas connection for primary backup power, but have the option to switch to propane or gasoline if the natural gas supply is ever compromised or if you take the generator to a remote location without a gas line.
Explore the ultimate in fuel flexibility with models that run on three fuel types: Best Tri-Fuel Generators
Critical Considerations for Natural Gas Generator Installation
Installing a natural gas generator, especially a permanent standby model, is not a DIY project. It involves specialized knowledge of electrical and plumbing systems and must comply with local building codes. Therefore, professional installation is mandatory.
Sizing and Power Requirements
The first step is determining the appropriate size, or wattage, for your generator. You must decide whether you want to power your entire home (whole-house backup) or just the most critical appliances like the furnace, refrigerator, well pump, and a few lights (essential circuit backup). Because natural gas has a slightly lower energy content (BTU) than liquid fuels, a natural gas-powered engine will typically produce about 10–15% less power than the same engine running on propane or gasoline. This derating must be accounted for during the sizing process.

Gas Line Infrastructure
The existing natural gas line supplying your home is likely sized for appliances like a furnace, water heater, and stove. A powerful generator requires a significantly higher volume of gas flow. In many cases, the utility or an authorized plumber will need to install a larger diameter gas line from the meter to the generator to ensure it receives an adequate supply for full-load operation. Without a properly sized line, the generator may sputter, stall, or fail to produce its rated output.
Code Compliance and Permits
Permitting is required for both the electrical and plumbing connections. Local codes dictate where the generator can be placed—usually a specific distance from windows, doors, property lines, and combustible materials—to address noise and exhaust safety. Working with a licensed contractor ensures that all local and national safety standards are met.
Natural Gas vs. Other Generator Fuels
While natural gas offers tremendous advantages, it’s helpful to see how it stacks up against the competition.
Natural Gas vs. Propane
Both are gaseous fuels, but their delivery is different. Propane requires an on-site tank that must be manually refilled. This limits run time but provides flexibility if the natural gas pipeline is damaged. Propane is stored as a liquid and has a higher energy density than natural gas, meaning a propane generator can produce slightly more power from the same engine size. However, the continuous, automatic supply of natural gas generally wins for long-term residential backup.
Natural Gas vs. Gasoline/Diesel
Gasoline and diesel generators are typically more powerful watt-for-watt and easier to transport, but they suffer from significant drawbacks. Fuel degrades over time, making long-term storage risky. They require constant refueling, which is difficult or impossible during a major outage. Furthermore, their emissions are significantly dirtier, and they are often louder than comparable natural gas models.
Pros of Natural Gas
- Continuous Fuel Supply: Unlimited run time from the utility line.
- Low Maintenance: No need to store or monitor fuel levels.
- Clean Burning: Lower emissions than liquid fuels.
- Convenience: Automatic start-up and shutdown with a standby unit.
Cons of Natural Gas
- Initial Cost: Standby units and installation are expensive.
- Power Derating: Generates 10-15% less power than the same engine on propane.
- Infrastructure Dependent: Relies on the integrity of the underground pipeline.
- Fixed Location: Standby units are permanent and non-portable.
Understanding Natural Gas as a Fuel Source
To fully appreciate the generator, it helps to understand the fuel. Natural gas is a naturally occurring hydrocarbon gas mixture consisting primarily of methane. It is a fossil fuel, but its extraction and distribution via extensive pipeline networks make it a highly accessible and efficient energy source globally. For more in-depth information on the composition and uses of natural gas, you can visit the Wikipedia page on Natural Gas.
Final Thoughts
The question, Can a generator run on natural gas?, moves far beyond a simple ‘yes’ and touches on a highly effective and popular power solution. Natural gas generators, particularly the standby models, offer unparalleled convenience, reliability, and peace of mind. While the upfront investment is higher than a portable unit, the benefit of having a truly continuous, hands-off power source during an emergency often justifies the cost. They are the ideal choice for those seeking a permanent, clean-burning, and maintenance-light backup system for their home or business.
By understanding the installation requirements and working with certified professionals, you can ensure your natural gas generator is ready to provide reliable power the moment you need it most.
Amranul is a highly experienced product review writer with a passion for helping readers make smart, informed purchasing decisions. Since 2018, he has specialized in thoroughly researching and analyzing a wide range of products to deliver honest, in-depth reviews. Amranul combines technical accuracy with clear, engaging writing to break down complex product features and highlight true user value. Look for his reviews to find reliable information and expert insights you can trust before you buy!





